Rabbit Ageing Signs
Rabbits mature and change physically and behaviorally. Rabbit owners must know the indicators of ageing in rabbits to provide the best care.
Decreased activity is a common rabbit ageing indicator. Rabbits may slow down and stop playing as they mature. Normal activity decreases.
Ageing rabbits lose appetite. Older rabbits may eat less and lose interest in their favourite delicacies. If your rabbit loses appetite, watch their weight and nutrition.
Grooming decreases as rabbits age. Older rabbits may neglect grooming, resulting in matted fur. To maintain healthy fur, brush your rabbit regularly.
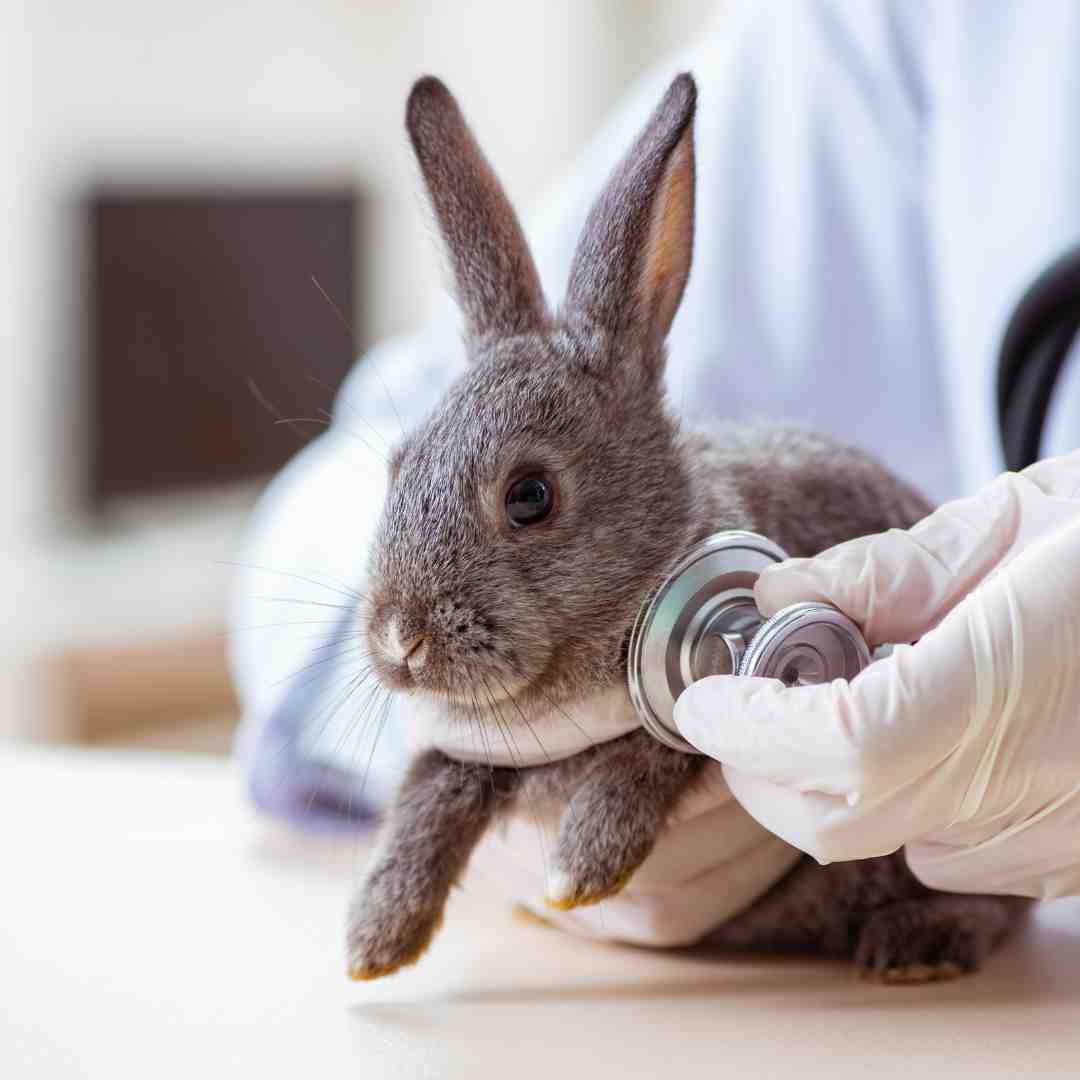
Finally, aged rabbits are more susceptible to illness and injury. Rabbits' immune systems weaken with age, making them more prone to sickness and infection. Rabbits need regular vet visits to stay healthy.
By understanding rabbit ageing, you can give your pet the finest care. Contact your vet if your rabbit's behaviour or look changes.
Spaying/Neutering Older Rabbits
Spaying and neutering older rabbits improves their health. Spaying and neutering rabbits can lower disease risk, aggressive behaviour, and even lifespan.
Spaying and neutering older rabbits reduces illness risk. Uterine cancer can kill unspayed female rabbits. Neutering male rabbits reduces testicular cancer risk. Spaying and neutering can also prevent ovarian cysts and uterine infections.
Spaying and neutering elder rabbits reduces aggression. Unneutered male rabbits may attack other male rabbits, while unspayed female rabbits may become territorial and violent. Spaying and neutering can lessen these behaviours and let rabbits coexist.
Finally, spaying and neutering older rabbits extends their longevity. Unspayed female rabbits may die from uterine cancer, whereas unneutered male rabbits may die from testicular cancer. Spaying and neutering can help rabbits live longer and healthier.
In conclusion, spaying and neutering elder rabbits improves their health. Spaying and neutering rabbits can lower disease risk, aggressive behaviour, and even lifespan. To ensure their health, older rabbits should be spayed or neutered.
How Long Do Rabbits Live?
Many people wonder about rabbit lifespans. Rabbits live 8–12 years, depending on breed and lifestyle.
Most domestic rabbits live 8–10 years. The Netherland Dwarf can live 12 years. Larger rabbits live longer.
Lifestyle, breed, and size affect rabbit lifetime. Indoor rabbits with regular veterinary care live longer than outdoor rabbits. Rabbits live longer with proper diet and activity.
Clean, well-cared-for rabbits can have long and healthy lives. Rabbits can be lifelong companions with proper care.
Breeding Older Rabbits
Breeding elder rabbits has perks and cons, making the decision tough. Older rabbits may be more calm and able to withstand breeding stress. However, they may have health difficulties and a shortened lifetime.
Pros
Breeding older rabbits has the benefit of a more balanced temperament. Breeding elder rabbits is less stressful and agitating. Older rabbits may comprehend breeding better, making it easier for them to have healthy offspring.
Breeding elderly rabbits may increase their lifetime. Older rabbits may produce more offspring over their lives, which can benefit long-term rabbit breeders.
Cons
Breeding elderly rabbits may increase health risks. Rabbits may have more health issues as they mature, making it harder to have healthy offspring. Older rabbits may live less, limiting their offspring.
Breeding elderly rabbits may reduce fertility. Older rabbits may produce fewer eggs than younger rabbits, making it harder to have numerous progeny.
Breeding elder rabbits has perks and cons. Older bunnies may live longer and have a more even temperament, but they may also have health difficulties and a shorter fertility window. Before choosing, consider the advantages and downsides.

Diet, Exercise, and Health for Ageing Rabbits
Diet and activity needs change as rabbits age. Understand these changes to keep your ageing rabbit healthy and happy. This page covers diet, activity, and health for ageing rabbits.
Diet
Ageing rabbits need a high-fiber, low-fat, low-sugar diet. This prevents obesity and other diseases. Give your rabbit fresh vegetables, hay, and a few pellets. Treats can make rabbits fat.
Exercise
Exercise keeps ageing rabbits active and healthy. Allow your bunny to roam and play. Encourage activity with toys and other stuff.
Health
Ageing rabbits need veterinary checkups. This will detect health risks early. Keep your rabbit's home clean and tidy. This prevents illness.
These tips will keep your ageing rabbit healthy and happy. Your rabbit can live long and healthy with proper care.